====================
This sermon was preached on Sunday, October 21, 2012, at St. Paul’s Episcopal Church, Medina, Ohio, where Fr. Funston is rector.
(Revised Common Lectionary, Proper 24B: Job 38:1-7,34-41; Psalm 104:1-9,25,37b; Hebrews 5:1-10; Mark 10:35-45. These lessons can be read at The Lectionary Page. At St. Paul’s Parish, the whole of Job 38 was read as the Old Testament lesson.)
The illustrations which follow in this sermon were presented as PowerPoint slides during the homily.
====================
This is our third installment in the sermon series The Patients of Job and we begin with a diagnostic question: What is half of 11?

Think about that for a while and we will return to this question in a moment. First, however, we need to catch ourselves up-to-date on the story of Job.
When we left Job last week, he and his friends Eliphaz, Bildad, and Zophar had had a long conversation about Job’s condition, his various misfortunes, and his own purity or blameworthiness; they then waxed philosophical about a hypothetical and stereotypical wicked man, being rather unclear whether that man was, in fact, Job. We were left with Job determined to take God to court where he would plead his innocence, but in something of a quandary because he was unsure where to find God.
Despite his confusion and bewilderment about the whereabouts of the Almighty, Job then spends the next nine chapters laying out his case. Bildad interrupts him briefly, but other than that the three friends do not speak further. There is a brief excursus in Chapter 28 about creation and wisdom, and scholars are unsure if Job is actually the speaker of that portion; it may be that this is one of the friends or even the narrator of the story speaking, but the text is unclear. When Job finishes, a newcomer begins to speak, Elihu the son of Barachel the Buzite. He comes on the scene unannounced, expresses his anger at Job and his friends because of their lack of understanding about God, and picks holes in some of their arguments. Most scholars think this a later addition to the book because Elihu’s speeches really add nothing and interrupt the flow between Job’s final speech and the appearance of the character God whose first speech in response to Job we heard today as our Old Testament reading. (I asked our lector to read the whole of Chapter 38, not simply the selected verses required by the Lectionary.)
My friend and colleague Steve _________, who is now the priest-in-charge of St. Bartholomew’s Episcopal Church in Mayfield Village, recently characterized the Book of Job, and this chapter of it in particular as “Job asking, ‘Why am I, a righteous man, suffering so?’ and God’s answer is ‘I am God and you are not.'” As Steve noted, that is not an entirely satisfying answer! I’ve often thought of the book and God’s answer in even less positive terms; it has frequently seemed to me that God’s response is (pardon the expression!), “Who the hell are you?”
But as I re-read the whole of the story in preparation for these sermons, and again as I have written each homily, I think that Steve and I have been wrong about this story. I don’t think God’s answer is either “I’m God and you’re not” or “Who the hell are you?” I think God’s answer is “What is half of 11?” And, again, I’ll come back to that.
I mentioned Chapter 28 earlier; that chapter really sets the background for God’s response to Job in this chapter. Chapter 28 has been called “one of the most exquisite poetic compositions of the entire Bible” (New Interpreters Bible, Vol. IV, Abingdon Press:1996, p. 528); I encourage you to read it! In Chapter 28, the speaker (whether Job or someone else) addresses the paradox of wisdom which cannot be found because it is everywhere. “Surely there is a mine for silver, and a place for gold to be refined,” it begins. (v. 1) “But where shall wisdom be found?” it asks, “And where is the place of understanding?” (v. 12) In what is really a hymn to wisdom and creation, the speaker sings of precious metals and prized gemstones, of the animals of nature, of the phenomena of weather, and of God who understands the way of wisdom because God “looks to the ends of the earth, and sees everything under the heavens.” (v. 24) Human beings, says the speaker, find wisdom through participation in creation in two particular ways. First, by what the speaker calls “the fear of the Lord,” a biblical term for piety or prayerful mindfulness; second, through “departure from evil,” which is to say moral action and uprightness. In these ways, human beings participate in the integrity of creation and understand the interrelatedness of all things; in a word, human beings find wisdom through creation and in creativity. This, then, is the background for what God says to Job in Chapter 38.
Job has laid out his legal case and made his arguments. God appears on the scene and rather than answer the lawsuit, he turns the tables on Job and starts asking him a lot of questions about nature. He asks about the seas, about wild animals, about storms and clouds and thunder, but says not a word about any of the points Job has laid out so carefully in his legal case . . . not a word. Instead, God’s address to Job is characterized by an “unrelenting use of rhetorical questions: ‘Who?’ ‘Where?’ ‘How?’ ‘What . . . can you . . . have you . . . do you know?'” (N.I.B., p. 598)
“What,” says God, “is half of 11?” Well, not actually. “What is half of 11?” is a question asked by my friend John O’Keefe. And, of course, we all know the answer, don’t we? Half of 11 is 5.5. You take 11; you divide it by 2; you get 5-and-a-half. Done.

But are we? In John’s book, The Church Creative (CreateSpace:2012), he suggests we ought to open ourselves to considering the question “What is half of 11?” from different and unexpected perspectives. (See also John’s website, The Church Creative.)
What if we visualize or understand this question not as “What is half of the number 11?” but “What is half of a character made up of two 1s, two vertical strokes?” Then half of 11 is . . .

. . . and the second half is . . .
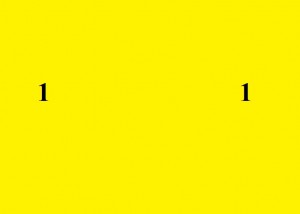
Or what if we think not in Arabic numerals but in the Roman numerals?

Then the first half of XI is an X . . .

. . . and the second half is an I.

Or, we could just slice the figure horizontally so that there’s a top half . . .

. . . and a bottom half.

Here’s another thought. Think in terms of words, not numbers. “What is half of e-l-e-v-e-n?”

Obviously, the first half is “e-l-e” . . .

. . . and the second, “v-e-n”.

Or, half of the word “eleven” is made up of the vowel “e” . . .

. . . and the other half is made up of consonants.

I suggest to you that God’s numerous rhetorical questions are meant to get Job to look at himself, his situation, his losses, and his current condition, from a different perspective, to understand God in a different way. God’s response to Job is like asking “What is half of 11?”
Just like us, when we read that question as being only and solely a math problem, Job has a particular way of seeing the world, a particular way of understanding reality, a particular way of understanding God. His frame of reference, if you will, was the social structure of his world, the village, clan, and family structure within which his life was lived. Job’s theological imagination was framed by that structure; the metaphors through which he sought to understand God came from that structure. Just as Job, acting as a person of honor, would hear and respond to a complaint from one of his employees or one of his children, so he believed God would hear and respond to his case. “Job’s image of God is developed out the highest and best values of his society, values that Job has always tried to embody.” (N.I.B., p. 556) This is fully in keeping with the Biblical tradition of “thinking about God by means of metaphors drawn largely from the realm of human relations.” (Ibid.) The problem, of course, is that such metaphors are limited and inadequate. God is not simply an ideal human person; God is “wholly other”, and God will not fit completely into the neat and tidy lines of our metaphors. Job is only partially correct about God. God will (and does) deal with Job as a loving Parent might deal with a child, but not in the way Job anticipates.
My daughter Caitlin recently shared with me an essay she wrote for one of her college courses. In it she related a story about my uncle, who was a very talented professional artist, teaching her to draw. This is her story:
My great uncle Richard was the first person to let me loose with a tool and tell me that I had the power to create “Art”. Sitting under an orange tree in my Grammy’s backyard, he handed me some colored pencils and told me to draw my favorite thing; at the time it was flowers. My geometric and organic patterns turned into a kid’s rendition of paisley. Once I got that flower thing down I wanted to move on to something more awesome. I couldn’t think of what to draw, so Uncle Richard decided to teach me a Surrealist technique to ease the imagination process. He told me to take a black pen, and without thinking about it too much, draw one continuous line all over the paper, “Just scribble it all up.”
After I scribbled the most extreme mess on the page, he told me to “make the ends meet.” I found the point at which I began my crazy doodle, connected the dots and then colored in the shapes between the lines with a myriad of color as he suggested. The great American painter Jasper Johns said the way to make art is to “Do something, then do something to that, then do something to that.”
My uncle had my daughter do something like this . . .
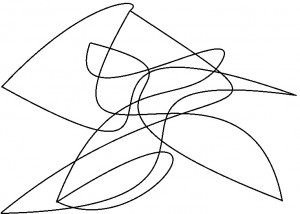
. . . and then do something like this to it.
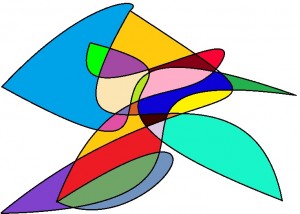
In this way, Uncle Richard taught Caitlin that she had (as she put it) “the power to create.” It must have worked; last year Caitlin painted this watercolor . . .
and, with it, won a scholarship at the University of Missouri.
God’s response to Job, all those rhetorical questions – “Who?” “Where?” “How?” “What . . . can you . . . have you . . . do you know?” – were God’s way of getting Job to “just scribble it all up,” of getting Job to stop being confined within the lines and limits and inadequacies of his metaphors, of getting Job to think creatively, of helping Job to find wisdom by participating in the integrity of creation and through understanding of the interrelatedness of all things. God’s response was not asking Job “Who the hell are you?” and God wasn’t answering his complaint with “I’m God and you’re not.” God was, however, saying, “I’m God but not in anyway you’ve ever considered, understood, or even imagined.” God was saying, “Neither I nor the world I created will fit within the neat lines of your metaphorical box.”
God’s response to Job is an invitation, and therein is the balm for us as “Patients of Job”, the prescription for whatever sickens our souls, for remedy for whatever ails our realities. God’s response is an invitation to Job and to us to participate in creation, to “scribble it all up,” to do something, then do something to that, then do something to that, to answer “What is half of 11?” in unexpected ways, to be creative in our problem solving. The answer to Job’s problem is not to sit on his pile of ashes moaning and complaining, disputing legalisms and “did I deserve it?”s with his friends; the answer to Job’s problem is not to sit on his pile of ashes framing legal arguments and preparing to sue God! The answer to Job’s problem is to get creative, to do something unexpected, to think outside the box. And that is spiritual medicine for us because, just like Job’s, neither our problems, nor our world, nor our God . . .
. . . will fit in our neat metaphorical boxes. Amen.


 Jonah’s a fool! Trying to flee “from the presence of the Lord.” As if! This lesson today is an interesting contrast to Sunday’s Eucharistic Lectionary reading from Book of Job (Job 23:1-9,16-17) in which Job was bewildered and confused because he felt unable to find God: “Oh, that I knew where I might find him, that I might come even to his dwelling!” (Job 23:2) Jonah, on the other hand, would be perfectly happy never to find, or be found by, God.
Jonah’s a fool! Trying to flee “from the presence of the Lord.” As if! This lesson today is an interesting contrast to Sunday’s Eucharistic Lectionary reading from Book of Job (Job 23:1-9,16-17) in which Job was bewildered and confused because he felt unable to find God: “Oh, that I knew where I might find him, that I might come even to his dwelling!” (Job 23:2) Jonah, on the other hand, would be perfectly happy never to find, or be found by, God. In last week’s reading from the Old Testament, you will remember, God gave Satan permission to test the righteousness of a man of integrity named Job. First all of Job’s possessions and his family are taken from him: his oxen and donkeys are carried off by Sabeans; his sheep are burned up in a fire; his camels are stolen by the invading Chaldeans; and the collapse of a house kills all of Job’s ten children. But Job, being a righteous man, does not curse God; instead, he shaves his head, tears his clothes, and says, “Naked I came from my mother’s womb, and naked shall I return there; the Lord gave, and the Lord has taken away; blessed be the name of the Lord.” Job does not sin or curse God. (1:21-22)
In last week’s reading from the Old Testament, you will remember, God gave Satan permission to test the righteousness of a man of integrity named Job. First all of Job’s possessions and his family are taken from him: his oxen and donkeys are carried off by Sabeans; his sheep are burned up in a fire; his camels are stolen by the invading Chaldeans; and the collapse of a house kills all of Job’s ten children. But Job, being a righteous man, does not curse God; instead, he shaves his head, tears his clothes, and says, “Naked I came from my mother’s womb, and naked shall I return there; the Lord gave, and the Lord has taken away; blessed be the name of the Lord.” Job does not sin or curse God. (1:21-22) I know two things today that I didn’t know earlier in the week. First, I know that people read our sign. I got two telephone calls and one email telling me that we had misspelled “patience” on the sign. Second, I know that people won’t believe you when you tell them you did it on purpose. But I really did name this sermon series “The Patients (P-A-T-I-E-N-T-S) of Job” for reasons that I hope will become clear very shortly.
I know two things today that I didn’t know earlier in the week. First, I know that people read our sign. I got two telephone calls and one email telling me that we had misspelled “patience” on the sign. Second, I know that people won’t believe you when you tell them you did it on purpose. But I really did name this sermon series “The Patients (P-A-T-I-E-N-T-S) of Job” for reasons that I hope will become clear very shortly.
 From time to time, people tell me that they have appreciated something I’ve said or done and I try to remember to say, “Thank you.” But inside, I really don’t think about compliments very much. It’s not that I don’t appreciated them, but I don’t do what I do to be complimented, and I really don’t think that I have much to do with it when whatever I do has gone well or had a positive impact on someone. I sort of take Paul’s attitude from the Letters to the Romans and the Galatians: “It is no longer I who live, but it is Christ who lives in me” (Gal. 20:2) and “I will not venture to speak of anything except what Christ has accomplished through me” (Rom. 15:18). So I do think, generally, that the answer to Eliphaz’s question is, “Yes.” Mortals can be of use to God. But there are times I would answer otherwise.
From time to time, people tell me that they have appreciated something I’ve said or done and I try to remember to say, “Thank you.” But inside, I really don’t think about compliments very much. It’s not that I don’t appreciated them, but I don’t do what I do to be complimented, and I really don’t think that I have much to do with it when whatever I do has gone well or had a positive impact on someone. I sort of take Paul’s attitude from the Letters to the Romans and the Galatians: “It is no longer I who live, but it is Christ who lives in me” (Gal. 20:2) and “I will not venture to speak of anything except what Christ has accomplished through me” (Rom. 15:18). So I do think, generally, that the answer to Eliphaz’s question is, “Yes.” Mortals can be of use to God. But there are times I would answer otherwise.  This morning I was struck by the absolutely opposite attitudes displayed in these two readings. The morning psalm invites God to try the worshipper; the first reading of the day demands the right to try God. I think these poles really do represent the spiritual pendulum on which most humans swing; they circumscribe our ambivalent and ambiguous relationship with the Almighty.
This morning I was struck by the absolutely opposite attitudes displayed in these two readings. The morning psalm invites God to try the worshipper; the first reading of the day demands the right to try God. I think these poles really do represent the spiritual pendulum on which most humans swing; they circumscribe our ambivalent and ambiguous relationship with the Almighty.  Wow! Does this look familiar? The second chapter of Job begins with a scene nearly identical to that which we considered yesterday. Satan (with other heavenly beings) presents himself in the heavenly throne room and, once again, God and Satan have a conversation about Job and, once again, the bet is made. In fact, it’s sort of “double down” time! Yesterday, I argued that although the Book of Job is fiction it (like the other forms of literature found in Holy Scripture) embodies truth.
Wow! Does this look familiar? The second chapter of Job begins with a scene nearly identical to that which we considered yesterday. Satan (with other heavenly beings) presents himself in the heavenly throne room and, once again, God and Satan have a conversation about Job and, once again, the bet is made. In fact, it’s sort of “double down” time! Yesterday, I argued that although the Book of Job is fiction it (like the other forms of literature found in Holy Scripture) embodies truth. A later selection from the Book of Job was called up by the Sunday Eucharistic Lectionary several weeks ago. In my sermon I said to the congregation that the Book of Job is fiction (which it is). You should have seen the look on one of my parishioners’ face! There’s a fellow in the congregation who is, shall we say, conservative with regard to the Bible. While I don’t believe he actually considers the Bible to be the inerrant word of God per se, he’s pretty sure that it is to be taken with the highest degree of certainty and words like “myth” or “fiction” applied to Scripture are not to his liking. I swear I thought he might have an apoplectic fit right there in his pew! But let’s be honest: do we really think that God and Satan are engaged (or have ever been engaged) in a game of chance involving the lives of human beings?
A later selection from the Book of Job was called up by the Sunday Eucharistic Lectionary several weeks ago. In my sermon I said to the congregation that the Book of Job is fiction (which it is). You should have seen the look on one of my parishioners’ face! There’s a fellow in the congregation who is, shall we say, conservative with regard to the Bible. While I don’t believe he actually considers the Bible to be the inerrant word of God per se, he’s pretty sure that it is to be taken with the highest degree of certainty and words like “myth” or “fiction” applied to Scripture are not to his liking. I swear I thought he might have an apoplectic fit right there in his pew! But let’s be honest: do we really think that God and Satan are engaged (or have ever been engaged) in a game of chance involving the lives of human beings? Our first reading this morning is from the Book of Job, which in the Jewish organization of Scripture is part of the Ketuvim or “Writings” and is considered one of the Sifrei Emet or “Books of Truth”, which is really quite interesting since it is generally acknowledged to be a work of fiction. It tells the story of Iyyobh (“Job”), who is described as a righteous man and who becomes the subject of a wager between a character called “Satan” and another character called “God”. I put it that way to underscore that this text is not relating to us any historical facts about God, or Satan, or a man named Job; it is, rather, telling a story in which characters representing God, Satan, and human beings in general help us to understand something about reality.
Our first reading this morning is from the Book of Job, which in the Jewish organization of Scripture is part of the Ketuvim or “Writings” and is considered one of the Sifrei Emet or “Books of Truth”, which is really quite interesting since it is generally acknowledged to be a work of fiction. It tells the story of Iyyobh (“Job”), who is described as a righteous man and who becomes the subject of a wager between a character called “Satan” and another character called “God”. I put it that way to underscore that this text is not relating to us any historical facts about God, or Satan, or a man named Job; it is, rather, telling a story in which characters representing God, Satan, and human beings in general help us to understand something about reality. Job wants answers about justice but God goes into a rant about the creation: the sea, the stars, the sky, the earth, the whole shebang! As the speech goes on for several chapters, God will talk about all the wild animals, even the ostrich, who is incredibly foolishness but very very speedy. What are we to make of this? Job wants fairness; he wants what’s right! And God’s answer is, “Hey! Look at that ostrich I made! It’s stupid but, wow, is it fast!” What’s the point?
Job wants answers about justice but God goes into a rant about the creation: the sea, the stars, the sky, the earth, the whole shebang! As the speech goes on for several chapters, God will talk about all the wild animals, even the ostrich, who is incredibly foolishness but very very speedy. What are we to make of this? Job wants fairness; he wants what’s right! And God’s answer is, “Hey! Look at that ostrich I made! It’s stupid but, wow, is it fast!” What’s the point?

